

Netstat –p X: with this command we can filter connections according to the protocol (TCP, UDP, tcpv6 or tcpv4.Netstat –o : shows the ID of each process on each connection.Netstat –n : This command, unlike the previous one, displays port numbers instead of names.Netstat –f : Displays the fully qualified domain name of remote addresses.Netstat –e : in this case we can see statistics about incoming and outgoing network packets on a network card.In this way we will be able to detect possible problems that affect a network. Netstat –a : allows us to know all the networks that are active or inactive at any given time.We are going to show which are the most used parameters to find specific details of the network. There are different parameters that we can take into account. With Netstat we can also solve some problems that may arise with our network connection.
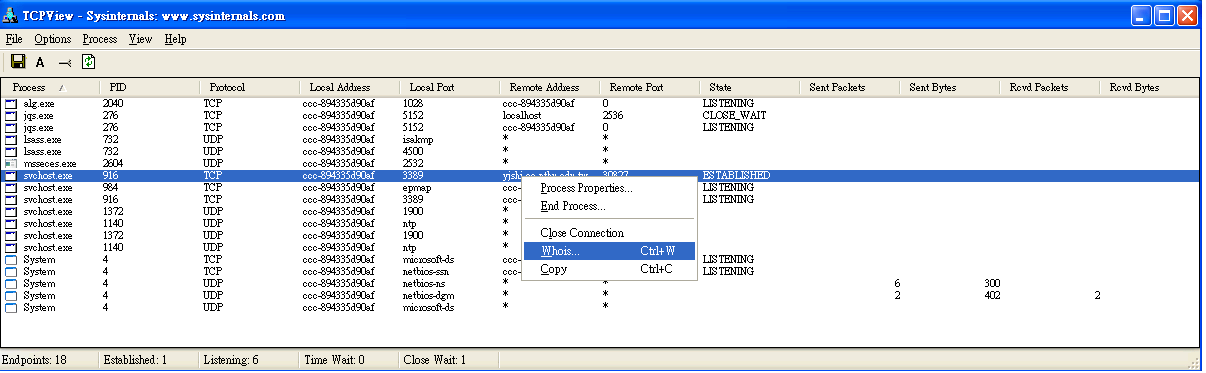
Programs like TCP VIEW, which was developed by the Microsoft division Windows Sysinternals, makes it possible for statistics to be displayed graphically. While the parameters of netstat’s commands (as well as their outputs) differ from system to system, when it comes to their functions, the various implementations are very similar.Įssentially, netstat is a command line program and for this reason doesn’t feature a graphical user interface.

netstat has been integrated into Linux since its debut in 1991 and has been present in Windows since the appearance of version 3.11 (1993), which could also communicate via TCP/IP with the help of extensions. In 1983, netstat was first implemented into the Unix derivative BSD (Berkley Software Distribution), whose version 4.2 supported the first internet protocol family, TCP/IP. It delivers basic statistics on all network activities and informs users on which ports and addresses the corresponding connections (TCP, UDP) are running and which ports are open for tasks. Netstat is derived from the words network and statistics it is a program that is controlled via commands issued in the command line.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
